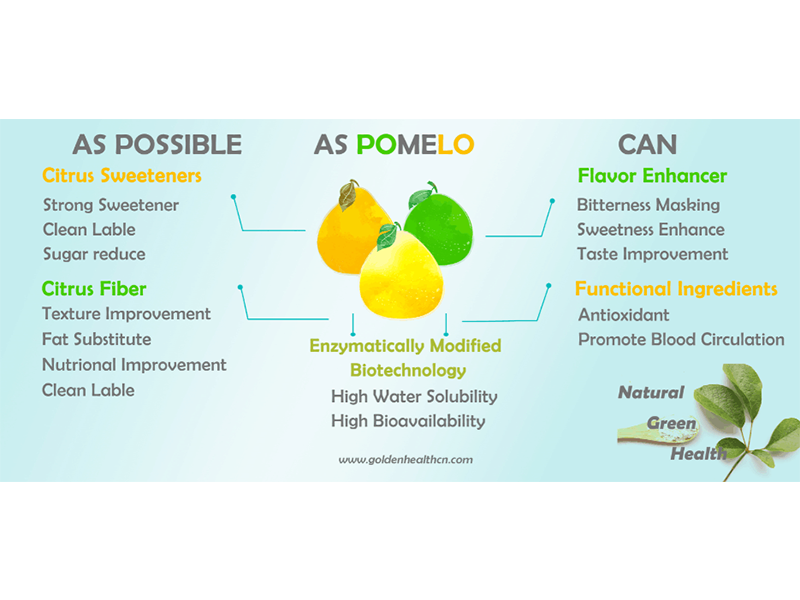
Introduction to popular science about hesperidin
Hesperidin is also called Chuanchenpi Su; dihydroflavonoid glycosides, molecular formula is C28H34O15, density: 1.65 g/cm3. This product is white or light yellow crystalline powder; it is odorless and tasteless. It is easily soluble in pyridine or dimethylformamide, but insoluble in ethanol or water.
Hesperidin has the functions of maintaining osmotic pressure, enhancing capillary toughness, shortening bleeding time, and lowering cholesterol. It is clinically used in the adjuvant treatment of cardiovascular diseases. It can cultivate a variety of drugs to prevent arteriosclerosis and myocardial infarction. It is a patent medicine One of the main raw materials of "Mai Tong". It can be used as a natural antioxidant in the food industry. It can also be used in the cosmetics industry.
Most of hesperidin is present in the waste of citrus processing. If the peel and fruit sac, the content of hesperidin in the mature peel and tissue is the highest, and the content in the juice and orange sac is lower by 1%-5%. The extraction methods of hesperidin include solvent extraction, alkali extraction and acid precipitation, carbon powder adsorption, and ion exchange. Among them, the alkali extraction and acid precipitation method has simple operation, low cost and high extraction rate. Orange peel is soluble in dilute alkali and pyridine and hot water above 70℃, slightly soluble in methanol, and almost insoluble in acetone, benzene and chloroform.
The extraction of hesperidin mainly utilizes the two phenolic hydroxyl groups contained in it to react with sodium ions in the solution under alkaline conditions to form sodium salt and dissolve it, and then acidify and cool to make it precipitate out of the solution. The extraction of hesperidin from citrus peel generally adopts hot extraction and soaking extraction methods, and the yield is not ideal. In recent years, research on ultrasonic extraction of active ingredients from natural plants has been extensively carried out, and certain progress has been made. Use hesperidin for extraction under alkaline conditions by ring-opening dissolution, and separation under acidic conditions by closed-loop precipitation. Increasing the amount of alkali during extraction can reduce the amount of ethanol, but the alkalinity should not be too large, otherwise, hesperidin is easy to be oxidized destroy.
Hesperidin has the functions of maintaining osmotic pressure, enhancing capillary toughness, shortening bleeding time, and lowering cholesterol. It is clinically used in the adjuvant treatment of cardiovascular diseases. It can cultivate a variety of drugs to prevent arteriosclerosis and myocardial infarction. It is a patent medicine One of the main raw materials of "Mai Tong". It can be used as a natural antioxidant in the food industry. It can also be used in the cosmetics industry.
Most of hesperidin is present in the waste of citrus processing. If the peel and fruit sac, the content of hesperidin in the mature peel and tissue is the highest, and the content in the juice and orange sac is lower by 1%-5%. The extraction methods of hesperidin include solvent extraction, alkali extraction and acid precipitation, carbon powder adsorption, and ion exchange. Among them, the alkali extraction and acid precipitation method has simple operation, low cost and high extraction rate. Orange peel is soluble in dilute alkali and pyridine and hot water above 70℃, slightly soluble in methanol, and almost insoluble in acetone, benzene and chloroform.
The extraction of hesperidin mainly utilizes the two phenolic hydroxyl groups contained in it to react with sodium ions in the solution under alkaline conditions to form sodium salt and dissolve it, and then acidify and cool to make it precipitate out of the solution. The extraction of hesperidin from citrus peel generally adopts hot extraction and soaking extraction methods, and the yield is not ideal. In recent years, research on ultrasonic extraction of active ingredients from natural plants has been extensively carried out, and certain progress has been made. Use hesperidin for extraction under alkaline conditions by ring-opening dissolution, and separation under acidic conditions by closed-loop precipitation. Increasing the amount of alkali during extraction can reduce the amount of ethanol, but the alkalinity should not be too large, otherwise, hesperidin is easy to be oxidized destroy.